Reverse Engineering Case Studies
Using Artec 3D Scanning Technology to Keep Dutch Royal Navy Ships in Ideal Condition
Summary: A challenging task for reverse engineering crucial parts for navy ships, for everything from hulls and engines all the way to onboard weapons systems. Usually no drawings or CAD files for these parts exist.
The Goal: By using the most advanced portable 3D scanning technology, new parts and modifications need to be made to high specifications on tight deadlines.
Tools Used: Artec Eva, Spider, and Artec Studio
By Yulia Ponomareva
Marinebedrijf Koninklijke Marine is a Dutch company responsible for the maintenance of all naval vessels and submarines of the Dutch Royal Navy, as well as M-class frigates of the Belgian Navy. The company also manufactures new parts for those ships and makes modifications of everything from the hulls to weapon systems and even engines.
“The use of the 3D scan technique is becoming more and more important because all ships of the Navy are coming to us for maintenance on a regular basis,” said Ben Jansen, CNC coordinator at Marinebedrijf Koninklijke Marine. “A lot of times we don’t have drawings or 3D CAD files of the things that need to be repaired or where we need to make new parts for existing systems.”
When they have no 3D data or drawings of the part, Marinebedrijf Koninklijke Marine brings in Artec 3D scanners to create a 3D image of the object, and the scan is then used to reverse engineer the object. The part is then replicated using 3D printing techniques, 3-5 axis milling, or 3D welding.
“We are now able to work a lot faster and more accurately,” said Ben Jansen. “Because we now have a complete 3D model, we have all the correct dimensions of every object. It results in a far more efficient way of working and it is faster, so we save a lot of money in these projects.”
The team no longer needs to make measurements with rulers and other tools. That approach was time-consuming and did not always yield accurate results. “Also it was common that you forgot to take certain measurements and had to go back to the ship again. That is now all over,” said Ben Jansen.
Marinebedrijf Koninklijke Marine uses the scanners for a wide range of vessels, for instance, the “Green Drake,” which is a boat of the former Queen of Holland. There are almost no drawings of this boat, and the team can now scan what they have and then make changes to the 3D digital model, such as when repairing cracks or replacing missing parts, and to machine new parts to bring the boat to perfect condition.
“By using the 3D scanning techniques, we can work faster and more efficiently, and of course we are now able to make parts that we could not make in the past or only through a very long and tedious process,” said Ben Jansen.
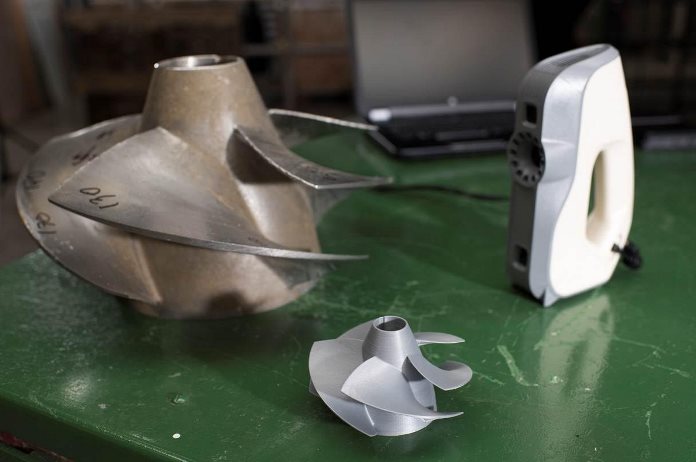
Another example is the project where they needed to repair the impeller of an LCVP (Landing Craft Vehicle Personnel). This boat sails half up onto the shore when dropping off marines, and when it needs to go in reverse, the LCVP moves backward and the impeller sucks in sand and rocks as well as water. These rocks slam against the impeller, resulting in small pieces breaking off.
The team scanned the impeller, and by using the resulting STL file they programmed their robotic welding system to perform accurate welding of only those exact spots where material needed to be added.
3D scanning is also useful for reverse engineering seats on FRISC-type high-speed boats, which can reach speeds of up to 80 km/h and are used for intercepting purposes.
Because of the high impact from the waves, the seats can occasionally crack and need repair. In a recent project, Marinebedrijf Koninklijke Marine scanned one of the seats with the Eva 3D imager and used the 3D information to create a reverse engineered mold, from which seats are now repaired.
“After collecting data, we are using all the tools available in Artec Studio to get a perfect model,” said Ben Jansen. “If we need to do modifications where Artec Studio does not have the necessary tools, such as adding on material to the 3D model, we export the file over to other software, where we can make the required changes.”
After post-processing, the model is usually exported to Spaceclaim, a CAD package for reverse engineering. And then a 3D file for 3D printing, milling, or 3D welding is created. If necessary, 2D and 3D drawings are made for tool shops within the Royal Navy.
“In all of this, the role of 3D scanning is growing rapidly,” said Ben Jansen. “We noticed that when you have a perfect tool like this, also other people suddenly see the impact and how easy it is to make a matching scan of an object. Then they want to use the scanner as well.”
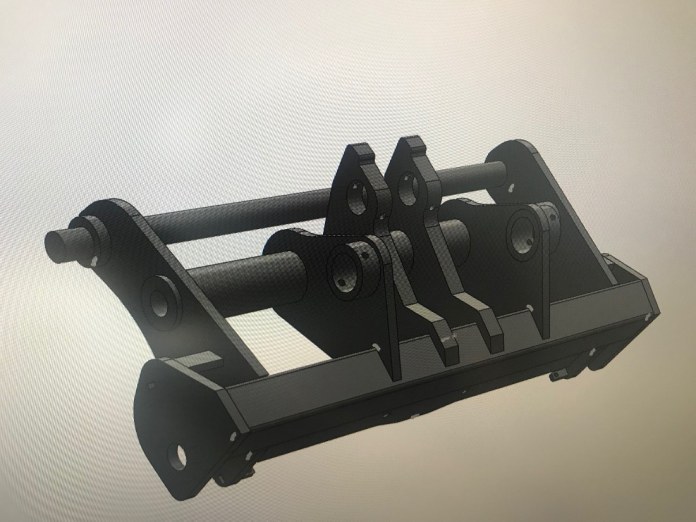
Artec Handheld 3D Scanner Reverse Engineering Legacy Tractor Equipment
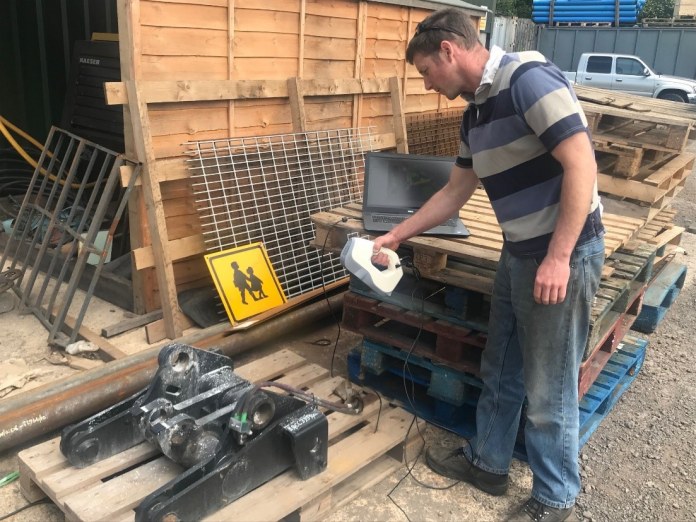
Taylor Attachments, a UK-based manufacturer of tractor headstock conversion brackets, frequently receives damaged equipment from its customers in need of restoration.
Normally, the company would sit down and spend hours manually drawing the parts needed to restore the piece of tractor equipment before making prototypes and revisions. The process altogether could take Taylor Attachments up to three weeks to complete: a lengthy and costly process.
The company came to Europac3D to look for a solution that would save it time and money in re-engineering legacy equipment. As a gold-certified reseller of Artec 3D scanners, Europac 3D recommended the Artec Eva 3D scanner: a fast, affordable and easy-to-use 3D scanner, perfect for capturing medium-sized objects.
Quick to set up and easy-to-use, with extremely fast scanning, a 536 x 371mm capture window and the ability to grab 16 frames per second, large objects can be digitized with speed and efficiency – the Artec Eva 3D scanner is the market-leader in hand-held 3D scanning.
The object is stitched together frame-by-frame on the screen in real-time, allowing the user to see exactly what they have captured as the user moves around the object being captured. Using the Artec Eva scanner, Taylor Attachments has reduced the time it takes to produce a digital model of the required equipment from weeks to just a single day.
“With Eva, it takes only about 20 minutes to scan an entire headstock, then another 20 minutes to post-process everything in Artec Studio – and after that, the 3D model from Studio is sent over to our in-house design team,” commented Mark Taylor of Taylor Attachments. “What they do is use the Xtract3D add-in for SOLIDWORKS to create a beautiful, highly-precise 3D model that’s 100% ready for protection. After that, it’s immediately sent over to one of our laser cutting partners.
“What we are looking at in terms of individual project time with Eva? Everything from start-to-finish in less than 24 hours. That’s it. Compare that with the seven days to two-to-three weeks it took us when we were doing it the old way. There’s simply no going back for us.”